As we celebrate the 10th anniversary of our initiative, we look back at our achievements so far and embrace the new challenges that lie ahead. And for this anniversary, we propose to share our analysis of 12 evidence-based conclusions about yogurt and health.
10th anniversary
The Yogurt In Nutrition Initiative (YINI) was established in 2013 to summarise our scientific knowledge on the health effects of yogurt. The activities of the YINI are guided by a Scientific Advisory Board of experts with a passion for advancing understanding of the links between diet and health.
Over the past decade, the YINI has organized 10 Global Summits on the health effects of yogurt as well as other major events at international conferences.
Since 2019, the YINI has taken on an additional role to address some of the most pressing concerns of our modern world: hunger, food sustainability, and planetary health. It became the Yogurt in Nutrition Initiative for Sustainable and Balanced Diets, with a new mission: “to promote and advance knowledge and practice on healthy sustainable diets and the importance of all food groups to meet nutritional needs across the lifespan, while respecting local food cultures, affordability, and accessibility”.
We celebrate the 10th anniversary of the YINI at a time of rapid scientific advancements that are highlighting exciting potential developments for managing health through yogurt as part of a sustainable and balanced diet.
Meanwhile, we are pleased to share our latest evidence-based conclusions so far in this Yogurt for Health publication, updated from the first edition that was published on the YINI 5th anniversary.
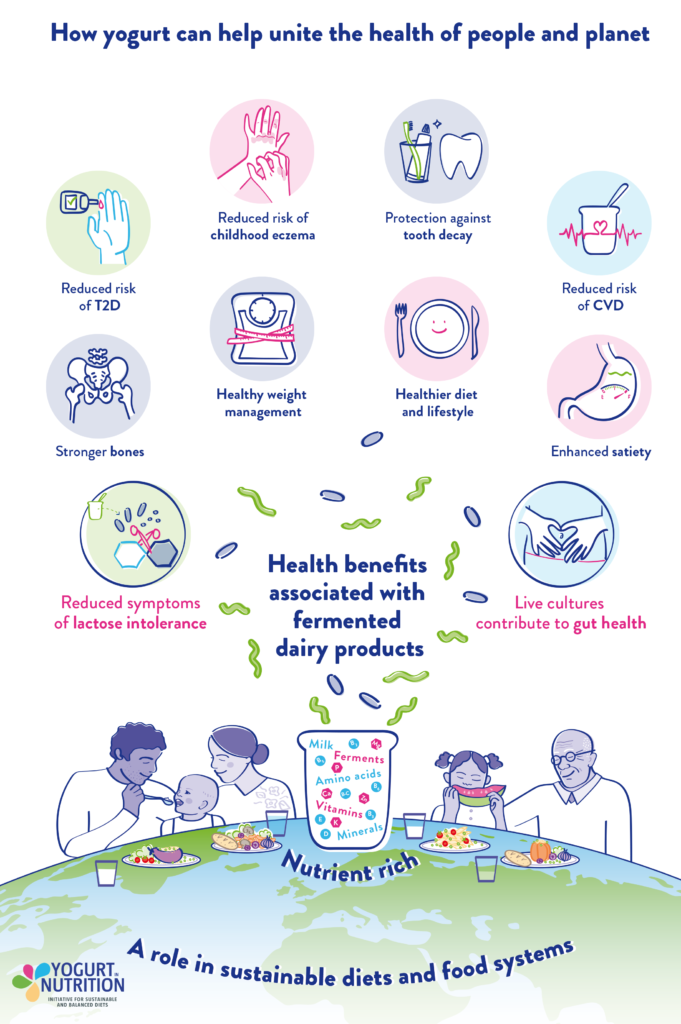
Evidence-based conclusions about yogurt and health
The booklet will review in details the main evidence-based conclusions related to yogurt and health.
You can also visit the YINI webpages on each topic, to discover recent publications, posts or other ressources:
- Yogurt in a nutrient-rich food, containing a wide range of macro- and micro-nutrients
- Yogurt consumption is associated with healthy diet and lifestyle and regular yogurt consumers of all ages tend to choose healthy diets and have healthy, active lifestyles
- Yogurt consumption is associated with stronger bones and reduced fracture risk
- Yogurt improves lactose digestion and reduces symptoms of lactose intolerance. Health authorities recommend yogurt as part of a healthy balanced diet for people with lactose maldigestion
- Yogurt with live cultures may contribute to gut health
- Yogurt can enhance satiety and may help to manage energy intake
- Eating yogurt is associated with healthy weight management
- Yogurt consumption is associated with reduced risk of Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome
- Yogurt consumption is associated with reduced risk of cardiovascular disease
- Eating yogurt is associated with a reduced risk of childhood eczema and allergies
- Eating yogurt may help protect against tooth decay and gum disease
- Yogurt can be part of sustainable diets and food systems