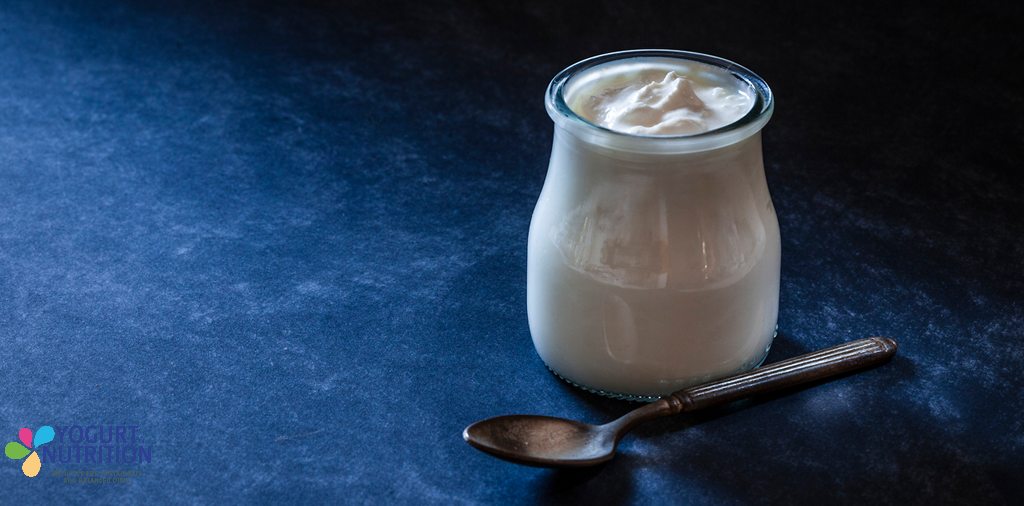
It is time to look at the “health and nutrition” topic we covered in 2020! We analyzed some publications on the effects of diets or yogurts and fermented milks on global health, prevention or in specific populations.
A review to examine the health effects of yogurt and fermented milk
It’s at the top of the shopping list for many health-conscious people but what exactly are the benefits of eating yogurt and where is the scientific evidence? This was the question addressed by US researchers. They carried out a thorough review of the medical literature for studies that examined the health effects of consuming yogurt and other fermented milk products.
The authors concluded that reduced risks of some cancers and type 2 diabetes, better weight control, and improved gut, heart and bone health were among the health benefits associated with eating yogurt or fermented milk products as part of a balanced and varied diet
Detailed information: Health benefits of yogurt and fermented milk revealed
A link between fiber and yogurt consumption and lung cancer
To go further, another publication showed that a diet high in fiber and yogurt has been associated with a reduced risk of lung cancer in a major study of over 1.44 million adults around the world.
This study pooled the data from 10 prospective cohort studies that recorded dietary information and cases of lung cancer in the USA, Europe and Asia, with a follow-up for an average of 8 years.
People with the highest intakes of both fiber and yogurt in their diet showed the greatest reduction in the risk of developing lung cancer. The risk was reduced by one-third compared with people who did not eat any yogurt and had the lowest intake of fiber.
Detailed information: could a yogurt rich diet be linked to reduced risk of lung cancer?
Effects on health and economics
Many studies have reported associations between dairy consumption and reduced risks of developing long-term diseases, including type 2 diabetes.
A US study suggested that increasing the daily dairy intake could help slash healthcare costs by curbing the burden of chronic disease. The authors weighed up all the pros and cons and estimated that, if all American adults increased their dairy intake to the recommended level of 3 servings/day, healthcare costs might be cut by US $12.5 billion each year.
Detailed information: Increasing dairy consumption could save billions in healthcare costs
Specific effects in babies: diarrhea and eczema
A Japanese research has shown an association between eating yogurt and a reduced risk of tummy bugs in babies. Over 82,000 mums with 1-year-old infants were asked to fill in a questionnaire to evaluate how often their baby ate yogurt and cheese, and about any episodes of gastroenteritis (vomiting and diarrhea) diagnosed by a doctor. The study showed that babies who ate yogurt at least 3 times/week were much less likely to have had vomiting and diarrhea than babies who ate yogurt less than once a week.
Detailed information: Yogurt consumption associated with fewer tummy bugs in babies
On another aspect, it seems that introducing yogurt during the first year of life is linked to a reduced risk of developing eczema and allergies.
In their study of maternal and infant health, New Zealander researchers provided mums with a daily probiotic or a placebo during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Either the mum or the biological dad of each baby had a history of asthma, hay fever or eczema. The mums were also asked to complete a questionnaire about the baby’s consumption of yogurt. The study results showed that infants who ate yogurt were significantly less likely to develop eczema and allergies than those who didn’t eat yogurt. 6–12 month-old infants who ate yogurt at least 2–6 times a week were significantly less likely to develop eczema and allergies than those who ate yogurt less than once a month. Living bacteria present in yogurt may play a role in this association.
Detailed information: Yogurt is associated with reduced risk of eczema and allergy in infancy
We invite you also to discover more through:
- Our infographic capsules about sugar in diet
- Some recent interesting scientific watch:
- Our infographic about the fermented milks around the World: rayeb, laban, labneh, ayran and amasi